- Computation of PI number. This example (http://siber.cankaya.edu.tr/ozdogan/ParallelComputing/cfiles/code15.c code15.c) evaluates
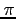 by numerically evaluating the integral
by numerically evaluating the integral
- The master process reads number of intervals from standard input, this number is then broadcast to the pool of processes.
- Having received the number of intervals, each process evaluates the total area of n/pool_size rectangles under the curve
- The contributions to the total area under the curve are collected from participating processes by the master process, which at the same time adds them up, and prints the result on standard output.
- This code computes PI (with a very simple method) but does not use MPI_Send and MPI_Recv. Instead, it uses collective operations to send data to and from all of the running processes.
- The routine MPI_Bcast sends data from one process to all others.
- The routine MPI_Reduce combines data from all processes (by adding them in this case), and returning the result to a single process.
- Run program for PI.
- Rewrite this code that replace the calls to MPI_Bcast and
MPI_Reduce with MPI_Send and MPI_Recv.
- Finding prime numbers. Write a complete program that finds the prime numbers up to 10000.
- The FIRST node should distribute the numbers to ALL BUT THE LAST node.
- The nodes which receive numbers should pass the number to the LAST node, which is continuously waiting for primes.
- When a node finishes its given numbers, it should pass "-1" to the LAST node.
- The program should end when the LAST node receives "-1" from all calculating nodes.
Cem Ozdogan
2010-11-22