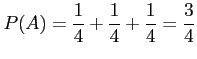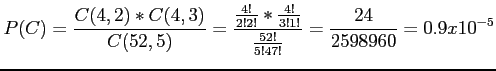- Perhaps it was man's unquenchable thirst for gambling that led to the early development of probability theory.
- What do we mean when we make the statements
- John will probably win the tennis match.
- I have a fifty-fifty chance of getting an even number when a die is tossed.
- I am not likely to win at bingo tonight.
- Most of our graduating class will likely be married within 3 years.
- In each case, we are expressing an outcome of which we are not certain, but owing to past information or from an understanding of the structure of the experiment, we have some degree of confidence in the validity of the statement.
- The likelihood of the occurrence of an event resulting from a statistical experiment is evaluated by means of a set of real numbers called weights or probabilities range from 0 to 1.
- The probability is a numerical measure of the likelihood of occurrence of an event, denoted by
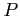 .
.
- To every point in the sample space we assign a probability such that the sum of all probabilities is 1.
- In many experiments, such as tossing a coin or a die, all the sample points have the same chance of occurring and are assigned equal probabilities.
- For points outside the sample space, i.e., for simple events that cannot possibly occur, we assign a probability of zero.
- Definition 2.8:

- In fact, P is a probability set function of the outcomes of the random experiment, which tells us how the probability is distributed over various subsets
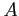 of a sample space
of a sample space  .
.
- Theorem 2.9:

- Example 2.27: In a poker hand consisting of 5 cards, find the probability of holding 2 aces and 3 jacks.
- If the outcomes of an experiment are not equally likely to occur, the probabilities must be assigned based on prior knowledge or experimental evidence.
- According to the relative frequency definition of probability, the true probabilities would be the fractions of events that occur in the long run.
- The use of intuition, personal beliefs, and other indirect information in arriving at probabilities is referred to as the subjective definition of probability.
Cem Ozdogan
2010-03-01