- Using a Signal Handler; completed. http://siber.cankaya.edu.tr/SystemsProgramming/cfiles/sigusr1works.csigusr1works.c
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
sig_atomic_t sigusr1_count = 0;
void handler (int signal_number)
{
time_t cur_time;
char *chartime;
int stat;
cur_time = time(NULL);
if ( cur_time == -1 ) {
perror( "Error getting time");
exit(1);
}
chartime = ctime(&cur_time);
printf( "SIGUSR1 received on %s", ctime(&cur_time) );
++sigusr1_count;
printf ("IN HANDLER: SIGUSR1 was raised %d times\n", sigusr1_count);
}
int main ()
{
int i,j;
pid_t child[5];
struct sigaction sa;
memset (&sa, 0, sizeof (sa));
sa.sa_handler = &handler;
sigaction (SIGUSR1, &sa, NULL);
child[1]=fork();
if (child[1] !=0)
printf("I am the parent \n");
else
{
sleep(5);
int pid = getpid();
printf("\n I am the first child with pid=%d \n",pid);
kill(pid,SIGUSR1);
child[2]=fork();
if (child[2] !=0)
printf("I am the parent of the second child \n");
else
{
sleep(5);
int pid = getpid();
printf("\n I am the second child with pid=%d \n",pid);
kill(getpid(),SIGUSR1);
}
}
printf ("IN MAIN: SIGUSR1 was raised %d times\n", sigusr1_count);
printf ("******************************************");
return 0;
}
- Analyze the code and output.
- What is the function of tje system call kill? Does It actually kill the process? If not, what is the functionality of that?
- Cleaning Up Children Asynchronously; completed. http://siber.cankaya.edu.tr/SystemsProgramming/cfiles/cleaningworks.ccleaningworks.c
#include <signal.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
sig_atomic_t child_exit_status;
void clean_up_child_process (int signal_number)
{
/* Clean up the child process. */
int status;
printf("I am in clenup function now and cleaning this child \n");
wait (&status);
/* Store its exit status in a global variable. */
child_exit_status = status;
printf("child_exit_status=%d with pid=%d \n", child_exit_status,
getpid());
printf("bla bla bla \n");
printf("-------------------------------------------------------\n");
}
int main ()
{
pid_t child_pid,child2;
/* Handle SIGCHLD by calling clean_up_child_process. */
struct sigaction sigchld_action;
memset (&sigchld_action, 0, sizeof (sigchld_action));
sigchld_action.sa_handler = &clean_up_child_process;
sigaction (SIGCHLD, &sigchld_action, NULL);
printf("Before child_exit_status=%d with pid=%d \n",
child_exit_status, getpid());
printf("-------------------------------------------------------\n");
child_pid=fork();
if (child_pid!=0)
{
sleep(5);
printf("I am the parent \n");
}
else
{
child2=fork();
if(child2!=0)
{
sleep(4);
printf("I am the first child with pid=%d and
child_exit_status= %d \n",getpid(),child_exit_status);
}
else
{
sleep(3);
printf("I am the second child with pid=%d and
child_exit_status=%d \n",getpid(),child_exit_status);
}
}
return 0;
}
- Comment the lines contains sleep out and observe the changes.
- Catching signals; http://siber.cankaya.edu.tr/SystemsProgramming/cfiles/sig_talk.csig_talk.c.
- Study the code to understand the signal catching mechanism.
- Thread Creation;
http://siber.cankaya.edu.tr/SystemsProgramming/cfiles/thread-create.cthread-create.c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/* Prints x's to stderr. The parameter is unused. Does not return. */
void* print_xs (void* unused)
{
while (1)
fputc ('x', stderr);
return NULL;
}
/* The main program. */
int main ()
{
pthread_t thread_id;
/* Create a new thread. The new thread will run the print_xs
function. */
pthread_create (&thread_id, NULL, &print_xs, NULL);
/* Print o's continuously to stderr. */
while (1)
fputc ('o', stderr);
return 0;
}
- You should break the execution by
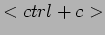 .
.
- Add a mechanism to catch or to handle the signal to the code.
- Passing Data to Threads; http://siber.cankaya.edu.tr/SystemsProgramming/cfiles/thread-create2.cthread-create2.c
- Study the code.
- Add the pthread_join functions.
- Execute several times to observe the changes in the output pattern.
- Thread Return Values; http://siber.cankaya.edu.tr/SystemsProgramming/cfiles/primes.cprimes.c.
- Study the code.
- Modify the code to print out all the prime numbers up to
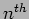 one.
one.
- Thread Attributes; http://siber.cankaya.edu.tr/SystemsProgramming/cfiles/detached.cdetached.c.
- Study the code.
- Modify http://siber.cankaya.edu.tr/SystemsProgramming/cfiles/thread-create2.cthread-create2.c to add detachstate attribute so that joining the threads will not be needed.
- Thread-Specific Data; http://siber.cankaya.edu.tr/SystemsProgramming/cfiles/tsd.ctsd.c
 .
.
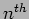 one.
one.